Insulin is crucial for glucose/sugar uptake by cells, so without proper insulin function, excess sugar builds up in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels, a key feature of diabetes.
There is no known cure for diabetes. Diabetes, both Type 1 and Type 2, is considered a chronic condition that requires lifelong management.
Effects of Diabetes on Overall Health
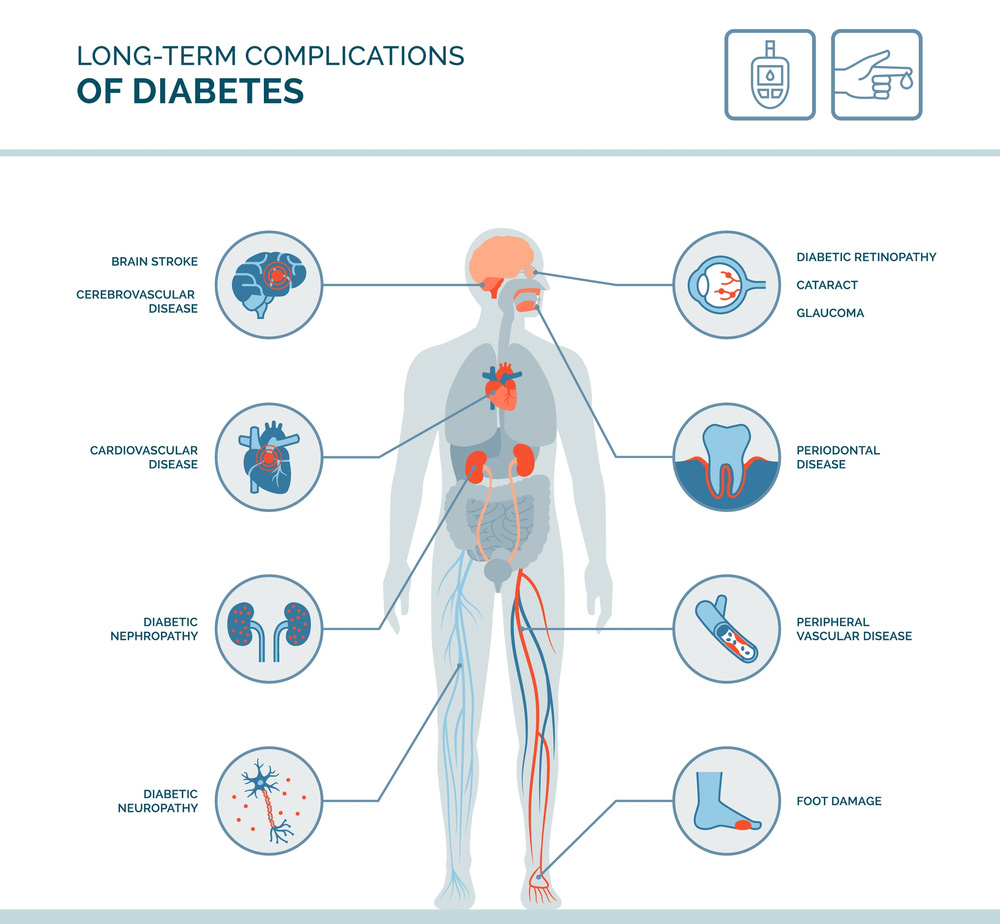
Diabetes can have a range of complications and side effects if not properly managed. Some common side effects and complications include:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular problems.
2. Kidney Damage: Diabetes can lead to kidney damage or failure (diabetic nephropathy).
3. Eye Problems: Diabetes can cause diabetic retinopathy, leading to vision impairment or blindness.
4. Nerve Damage: Peripheral neuropathy may result in tingling, pain, or numbness in the extremities.
5. Foot Complications: Poor circulation and nerve damage can contribute to foot problems, sometimes leading to infections and amputations.
6. Skin Conditions: Diabetes may increase the risk of skin infections and slow wound healing.
7. Hearing Impairment: There is an association between diabetes and an increased risk of hearing loss.
8. Altered Immune Function: Diabetes can weaken the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections.
9. Mental Health: Diabetes may contribute to mental health issues such as depression and anxiety.
10. Gastrointestinal Issues: Diabetes can affect the digestive system, leading to issues such as gastroparesis (delayed emptying of the stomach).
11. Sleep Apnea: There is an increased risk of sleep apnea in individuals with diabetes.
Diabetes Treatment Options
1. Medication:
- Type 1 Diabetes: Individuals with Type 1 diabetes require insulin therapy, usually through injections or an insulin pump.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Medications may include oral medications that increase insulin sensitivity, stimulate insulin production, or reduce glucose absorption. In some cases, insulin therapy may be prescribed.
2. Healthy Eating:
- Adopting a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels.
- Focus on whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Limit intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and refined carbohydrates.
3. Regular Physical Activity:
- Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity and regulate blood sugar levels.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with strength training exercises.
4. Blood Sugar Monitoring:
- Regularly check blood sugar levels using a glucometer as advised by healthcare professionals.
- Monitoring helps in understanding how different foods, activities, and medications affect blood sugar.
5. Weight Management:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is important, especially for individuals with Type 2 diabetes.
- Weight loss can improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control.
6. Stress Management:
- Chronic stress can impact blood sugar levels. Practices such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress.
7. Regular Medical Check-ups:
- Regular visits to healthcare professionals are crucial for monitoring overall health, adjusting medications, and addressing any complications.
8. Medication Adherence:
- It’s important to take prescribed medications as directed by healthcare providers.
9. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM):
- CGM devices provide real-time information about blood sugar levels, helping individuals make timely adjustments to their treatment plan.
10. Diabetes Education:
- Learning about diabetes, its management, and lifestyle choices is essential for effective self-care.
Diabetes reversal diet
A well-balanced and nutritious diet is crucial for individuals with diabetes. Below is a general food chart for someone with diabetes in India. It’s important to note that individual dietary needs may vary, and consulting with a registered dietitian or healthcare professional is recommended for personalized advice.
1. Carbohydrates:
- Choose complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index (GI), such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables.
- Limit refined carbohydrates and sugars.
- Examples: Brown rice, quinoa, whole wheat roti, oats, lentils, chickpeas, and plenty of vegetables.
2. Proteins:
- Include lean protein sources to help maintain muscle mass.
- Examples: Fish, skinless poultry, tofu, legumes, low-fat dairy products, and paneer (cottage cheese).
3. Fruits:
- Opt for fruits with a moderate GI and consume them in moderation.
- Examples: Berries, guava, papaya, apple, pear, and citrus fruits.
4. Vegetables:
- Emphasize non-starchy vegetables.
- Examples: Spinach, broccoli, cauliflower, bell peppers, bitter gourd, and leafy greens.
5. Fats:
- Choose healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil in moderation.
- Limit saturated and trans fats found in fried foods, processed snacks, and fatty cuts of meat.
6. Dairy:
- Opt for low-fat or skim dairy products.
- Examples: Low-fat milk, yogurt, and paneer.
7. Snacks:
- Choose snacks with a balance of protein and fiber to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Examples: Nuts, seeds, roasted chickpeas, cucumber slices with hummus, or a small serving of fruit.
8. Beverages:
- Drink plenty of water.
- Limit sugary beverages and opt for unsweetened options.
- Herbal teas and black coffee (without added sugar) are good choices.
9. Portion Control:
- Pay attention to portion sizes to manage calorie intake and blood sugar levels.
10. Meal Timing:
- Aim for regular meal times and consider spacing meals throughout the day to help regulate blood sugar.
Elevate your well-being at DfabU: Nourish your body, lose weight, and thrive with Dietician Deepak Khera. Start your healthy transformation today – call 83602 57379!


